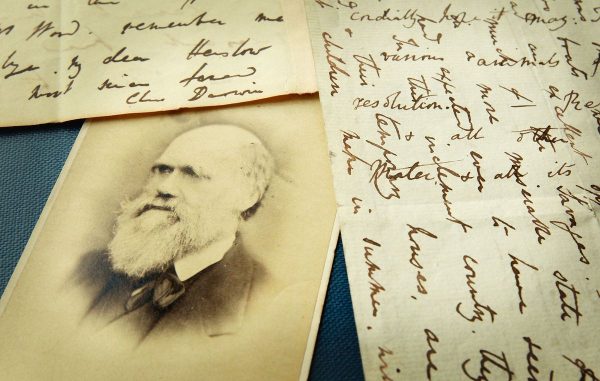Science has been so wrong about women, and it’s time to fix it

It’s easy to assume that just because something is scientific it’s true.
That doesn’t account for the glut of conflicting findings both in academia and industry over the past century and how social constructs have impacted scientific judgement.
It also doesn’t account for the fact that science has been — and in some cases continues to be — dominated by men and their often collective worldview. SEE ALSO: First-of-its-kind study reveals harassment faced by women of color in space science
Just think about how that male dominance has impacted the way the scientific community has represented women — both in terms of female participation in and contribution to science.
A new book is turning all that history on its head. Inferior by British science writer Angela Saini delves into the many ways that “science has got women wrong” using “new research that is rewriting the story.” The new book attempts to provide an alternative view of science where women are included, rather than excluded.
“From intelligence to emotion, for centuries science has told us that men and women are fundamentally different. But this is not the whole story,” writes Saini. Inferior “sheds light on controversial research and investigates the ferocious gender wars in biology, psychology and anthropology.”
The book is indeed a reminder of the ways in which science has been used to reinforce or break down sexist stereotypes. We dismantle nine of them below:
Women are intellectually inferior to men
Despite being the man behind the theory of evolution, Charles Darwin had some pretty un-evolved views about women.
In the book, Saini tracks down a series of letters to and from Darwin shortly before his death in 1881. An American women’s rights activist named Caroline Kennard wrote to Darwin asking him to set the record straight about his most important works — On the Origin of the Species(1959) and The Descent of Man (1871) — which at the time were being used to support the argument that women were inferior to men “based upon scientific principles.”
“In the letter Kennard naturally assumes that a genius like Darwin couldn’t possibly believe that women are naturally inferior to men. Surely his work had been misinterpreted?” writes Saini.
Darwin wrote back, and wow, did he deliver: “I certainly think that women though generally superior to men [in] moral qualities are inferior intellectually,” he told her.
“Darwin’s scientific ideas mirrored society’s beliefs at the time and they colored his judgement of what women were capable of doing. His attitude belonged to a train of scientific thinking that stretched back at least as far as the Enlightenment,” writes Saini.
Sure, Darwin’s was a product of his time. But is that an excuse? As the book outlines, there were plenty of forward-thinking individuals back in the day — like Albert Wolfe, Caroline Kennard, and Eliza Burt Gamble.
Women have not contributed much to science
It’s a massive — but often used — generalization that men have contributed more to science than women have in the past century.
The truth is men have dominated the scientific narrative of the past 100+ years and this is largely because women have not had the same access to the field.
Keep in mind, it wasn’t until 1893 that women first got the right to vote in New Zealand and that right didn’t extend to the UK and U.S. until 1918 and 1920, respectively. Women were still fighting for their fundamental rights. “Taking on this male scientific establishment wasn’t easy. For nineteenth century women everything was at stake,” writes Saini.
“It took until well into the 20th century for women to be granted full degrees in many of the world’s universities. Where I studied engineering, in Oxford, they didn’t allow women to become full members until 1920, but many others were even slower than that,” says Saini. “Europe’s scientific academies were even worse. Marie Curie won two Nobel Prizes, and was still rejected by the French Academy of Sciences in 1911. So we have to remember that women are only just catching up from a long legacy of deliberate exclusion. It’s only been a few generations since they’ve even had access to the same educational opportunities as men.”
The Victorian suffragist movement urged women to educate themselves to stand a chance of taking on the sexist debate about inferiority.
One of the trailblazers of the time was the scientific suffragist Eliza Burt Gamble. Her book The Evolution of Woman (1894 and revised in 1916) lays out Darwin’s inconsistencies and double standards with regard to gender.
Gamble says that inequity in women’s contributions to intellectual work were more a result of inequality than innate inferiority. Women weren’t allowed to develop their scientific talents, and making assumptions about their abilities based on how they happened to be treated by society was narrow-minded and dangerous.
Eliza Burt Gamble: writer, freethinker, feminist. #GetPissedGetActive #shepersisted#letlizspeak pic.twitter.com/6eOPQ1xtKj
— JaySandlinWriter (@JSandlinWriter) February 8, 2017
So there was a counter argument to Darwin’s proclamations about gender at the time, but they weren’t given equal recognition because they came from a woman.
Gamble’s “army of readers and the support of fellow activists couldn’t win biologists around to her point of view,” writes Saini. “Her arguments were doomed never to fully enter the scientific mainstream, only to circulate outside it.”
In the face of adversity, women have been resourceful and strategic. “In the past, if women wanted to practice science, they sometimes became assistants to their scientist husbands or fathers, their contributions subsumed under their names,” says Saini. “These lost women of science are slowly being rediscovered, but it is tragic that their hard work and talent wasn’t recognised at the time.”
Women are natural ’empathizers’ and men are ‘systemizers’
A 2002 study carried out on babies unveiled a controversial “empathizing-systemizing theory.”
It basically said that the female brain is hardwired for empathy while the male brain is built for analyzing and building systems like cars and computers.
This apparently explains the fundamental differences in the hobbies that men and women chose, according to psychologist and neuroscientist Simon Baron-Cohen. For example, men like to repair motorbikes and women prefer to attend coffee mornings in their spare time.
This may come as a shock, but this study has been debunked time and time again. Most notably, a team of psychologists poured cold water on it in 2007, picking out a huge number of problems with the hypothesis.
Men have heavier brains, meaning they’re more intelligent
Scientific study after scientific study has found that there is a 5 ounce difference between male and female brains.
This difference in weight has been used by neuroscientists to reinforce the argument that male and female brains are fundamentally different. It has also been used to imply a difference in intelligence.
This was challenged in the late 1800s by the American teacher and writer Helen Hamilton Gardener, the pen name for Alice Chenoweth Day.
Working alongside Edward Spitzka (who became president of the American Neurological Association), Gardener observed that the weight of a person’s brain couldn’t be a measure of intelligence. It was the ratio of body weight, or body size to brain size, that was important.
But as Saini writes: “The fight over those missing five ounces was a bitter one and it was never resolved in Helen Hamilton Gardener’s lifetime.”
That hasn’t stopped the argument from rearing its head over and over again.
In fact, only a few weeks ago a controversial study by scientists at Erasmus University in Rotterdam found that men have higher IQs than women because they have bigger brains. After using the latest scanning technology to measure the brain volumes of 896 people, Professor Dimitri van der Linden, who led the study, said: “We found that the average IQ of men was about four points above that of women. So if men had an average score of 100, women would score 96.”
The study has reignited the controversial debate. But Saini has been quick to stand her ground, telling The Sunday Times: “It is scientifically well established that there is no difference on average in general intelligence between women and men. It’s also well known that women have, on average, slightly smaller brains than men because they are, on average, slightly smaller in size. This paper does not disprove these facts.”
Women are the weaker sex
On average men are 6 inches taller and have twice the upper body strength of women. But to classify women as the weaker sex, doesn’t tell the whole story. Women are actually stronger at birth and they live for longer.
“Pretty much at every age, women seem to survive better than men,” aging expert Steven Austad tells Saini in the book.
Research shows that, from birth, girls are statistically more robust than boys. Joy Lawn, at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine found that boys are around 10 percent at greater risk of dying than girls in the first month of their lives.
Clinical trials predominantly focus on men
Because of the complexity of the female body and the fluctuation of sex hormones, it has simply been cheaper and easier for the pharmaceutical industry to try out new medication on men during clinical trials.
It’s been estimated that women are 1.5 times more likely to develop an adverse reaction to a drug than men.
“Let’s face it, everyone in the biomedical community has spent their lives studying one sex or the other. And it’s usually males,” Steven Austad, Chair of Biology Department at the University of Alabama in Birmingham, said in an interview.
Some medications have even been taken off the market after having an adverse effect on women. In 2000, the U.S. Government Accountability Office found that eight out of 10 prescription drugs taken off the market since 1997 posed greater health risks to women than men.
This is pretty egregious but thankfully things are improving. “There has been a huge movement in the United States to include women in clinical trials for new drugs and the imbalance is being gradually corrected,” says Saini. “The hope is that in the future, we won’t see the kind of mistakes that we’ve seen in the past because females will be better represented, not just in the drug development process, but in research as a whole.”
Penises have been studied in far greater detail than female organs
So much is known about the male body. But vaginas have more or less been ignored.
Even when you think about the solutions provided for period pains — women are often given an overly simplistic solution. Take ibuprofen.
Sexist stereotypes have been been cited as the root cause for why period pains are not afforded the same level of importance by doctors as other ailments, because women are somehow “exaggerating” or being “dramatic.” “Men don’t get it and it hasn’t been given the centrality it should,” John Guillebaud, professor of reproductive health at University College London, told Quartz. “I do believe it’s something that should be taken care of, like anything else in medicine.”
Period pain is officially as bad as a heart attack – so why have doctors ignored it? The answer is simple https://t.co/T8GfNWcmJ3
— Independent Voices (@IndyVoices) May 15, 2017
“In animal biology across all species there is more research on male sexual organs than there is on female ones … Medicine research has neglected problems that affect only women,” adds Saini.
Women are less promiscuous and less open to casual sex
Women are naturally more monogamous and more selective about who they chose to shack up with, right? Not necessarily. Social context has a big role to play.
A 1978 study at Florida State University found that women and men were as likely to go on a date with a stranger but none of the women would sleep with one.
In 2015, scientists in Germany carried out a similar study with some interesting changes to the results. Women were found to be just as “up for it” as men, but fear of judgement, damage to reputation, or concerns about physical safety played a role in their decision. TL;DR: When society isn’t judging, women’s sex drive rivals mens.
So cultural and societal norms play a big role in women’s behaviour. Saini’s book explains how it is as acceptable for women to have affairs as men in many indigenous populations, for example.
There is also plenty of evidence from the animal kingdom to challenge that preconceived notion of coy, chaste, females. Forty years ago the primatologist Sarah Blaffer Hrdy found that female Langur monkeys can benefit from mating with more than one male.
Menopause happens because men don’t find older women attractive
“In evolutionary psychology some male researchers insist that the female menopause evolved because no man of any age would find an older woman attractive,” Saini says in the above video.
She’s referring to evolutionary biologist Rama Singh from the McMaster University of Canada, who along with Richard Morton and Jonathon Stone, made global news headlines in 2013 when a paper (published in PLOS Computational Biology) said older women become infertile because men don’t find them attractive. At the time, an article by Stone ran with the headline “Putting the Men in Menopause.”
We’re calling B.S. on this one and we’re not alone.
The theory that women dry up because they’re no longer desirable to men was shut down from scientists of other research disciplines.
“The reason men don’t prefer post-menopausal women is that they’re post-menopausal and they can’t get pregnant, not the other way round,” said Rebecca Sear, a scientist at the LSHTM.
Not all ideas are good or decent. Not all science is objective or neutral. Not all “evidence” is what is presents itself to be. Thankfully there are authors like Angela Saini challenging what we *think* we know.